
Introduction
Behind each good tyre driving on the road is a demanding and intense production process. In a top tire factory in India, performance was quietly being compromised—not due to machine breakdown, but due to operator fatigue. With the heavy-duty Tire Building Machines (TBM) to handle, operators were exhibiting signs of fatigue that manifested in variable output, increased losses, and operational inefficiencies.
To address this, the company turned to Production Modeling India (PMI) for a comprehensive industrial engineering study focused on fatigue reduction and productivity enhancement.

Client’s Challenge
• Inconsistent output from TBM machines due to operator fatigue
• Low productivity, despite skilled labor
• Losses arising from unoptimized manpower deployment
• A lack of systemized methods to balance workload during long shifts
Reducing Fatigue by 38% and Boosting Output: PMI's Industrial Engineering Study Transforms Tyre Building Operations
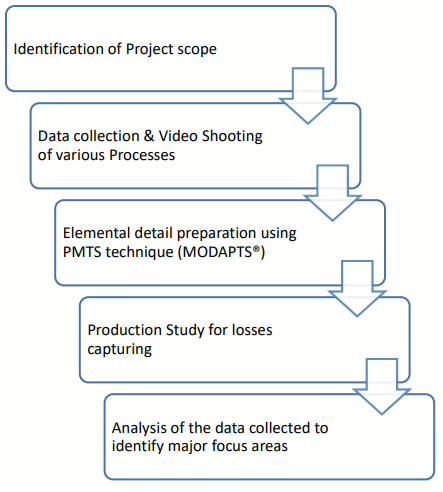
PMI’s Strategic Approach
PMI framed the study with intent and purpose:
- Scope Identification – Identifying major pressure points on the TBM line
- Data Collection & Video Recording – Tracking operator movement, cycle times, and rotation of job
- PMTS Analysis (MODAPTS®) – Quantifying elemental work content to normalize tasks
- Production Study – Confronting real-world losses and bottlenecks with time-motion study
- Data Analysis – Reconstructing fatigue trends and their influence on cycle time variation
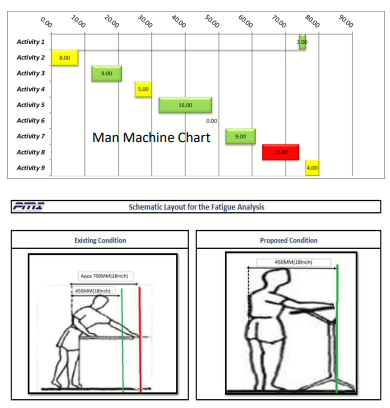
It was not just a matter of work time, but also of how that work was rotated, relieved, and distributed.
Key Findings & Recommendations
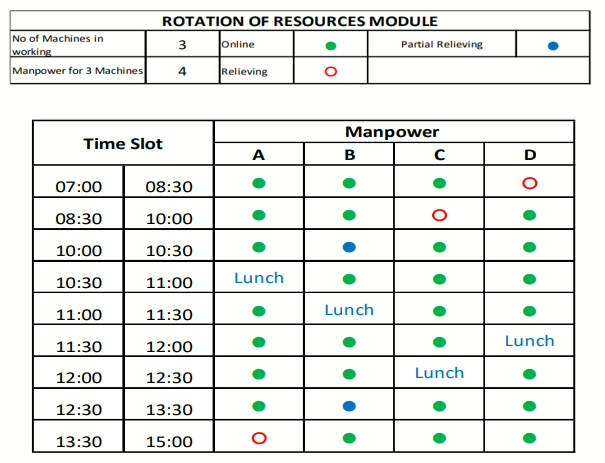
PMI implemented an organized Rotation of Resources (RoR) module that facilitated switching tasks periodically between machines and departments for a shift. This helped to eliminate repetitive strain and permitted muscles and even minds to rest.
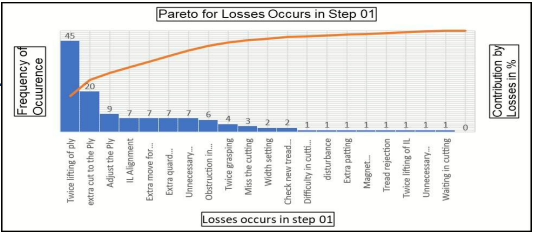
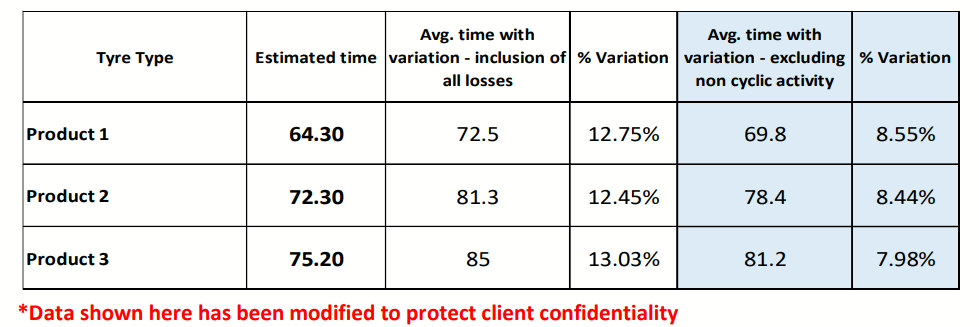
• The mean cycle time variation due to fatigue was as high as 13% in certain products.
• After rotation, variation fell below 8%, enhancing uniformity.
• Time-opposition man-machine chart was constructed dynamically to efficiently allocate manpower among machines.
• Strategic relieving patterns were suggested to permit partial resting without stopping operations.
Conclusion
The answer was not more labor or quicker equipment—it was more intelligent rotation, scheduled breaks, and matching human capability with achievable expectations. By integrating lean thinking and realistic scheduling, PMI enabled the client to unlock improved performance from existing resources. For this tire manufacturer, addressing fatigue wasn't merely about comfort—it became the quickest route to improved productivity.
